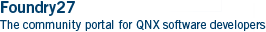| wiki1202: SMPInitialisation |
SMP Initialisation#Booting an SMP system involves an elaborate dance between cpus. The following shows the sequence of events in terms of the various pieces of code involved:
This shows only the sequence from initial execution of the startup program:
cpu0
----
_start(): [startup]
. set up C environment
. jump to _main()
_main():
. board_init()
. setup_cmdline()
. cpu_startup()
. init_syspage_memory()
- allocate generic sections
- cpu_init_syspage_memory()
. main():
- process cmdline
- select_debug()
- init_raminfo()
- init_smp():
. allocate syspage smp section
. board_smp_init()
- init_mmu()
- init_intrinfo()
- init_qtime()
- init_cacheattr()
- init_cpuinfo()
. allocate syspage cpuinfo section
. init_one_cpuinfo(0):
- set up cpu0 cpuinfo section fields
- add_cache() for cpu cache(s)
- init_hwinfo()
- init_system_private():
. load IFS image(s)
. load bootstrap executables
. smp_hook_rtn() --> start_aps(): cpuN
for each cpu { ----
board_smp_start(N, smp_start) ------> smp_start():
wait for cpuN to clear cpu_starting . set up C environment
: . board_smp_adjust_num()
: . cpu_startup()
: . init_one_cpuinfo(N):
: - set up cpuN cpuinfo section fields
: - add_cache() for cpu cache(s)
:<-------------------------------------- . clear cpu_starting
} . wait for syspage_available == N
. alloc_syspage_memory(): :
- cpu_alloc_syspage_memory(): :
. allocate memory for syspage/cpupage(s) :
. set syspage/cpupage pointers :
- write callout routines to syspage memory :
. write_syspage_memory() :
- write syspage sections to syspage memory :
- cpu_write_syspage_memory(): :
. flush icache if necessary for callout code :
. smp_hook_rtn() --> transfer_aps(): :
for each cpu { :
set SYSPAGE_ENTRY(smp)->pending :
set syspage_available = N ----------------> . cpu_startnext(N, smp_spin_vaddr)
wait for SYSPAGE_ENTRY(smp)->pending == 0
: smp_spin(): [callout code]
: <---------------------------------------- . clear SYSPAGE_ENTRY(smp)->pending
} . wait for SYSPAGE_ENTRY(smp)->start_addr != 0
. startnext(): :
- cpu_startnext(0, kernel entry point) :
:
_start(): [kernel] :
. set stack pointer :
. jump to _main() :
:
_main(): :
. syspage_init(): :
- set variables pointing at syspage sections :
- cpu_syspage_init() :
. set_inkernel(INKERNEL_NOW|INKERNEL_LOCK) :
. set up cmdline args :
. kernel_main(argc, argv, envv): :
- process cmdline args :
- init_memmgr() :
- init_traps() :
- memmgr.init_mem(0) --> vmm_init_mem(0) :
. initialise global VM data structures :
- init_critical_heap() :
- init_objects(): :
. allocate various data structures :
. allocate initial PROCESS structure :
. allocate idle thread for each cpu :
- timer_init() :
- interrupt_init(): :
. set up interrupt data structures :
. cpu_interrupt_init(): :
- generate interrupt dispatch code :
- plumb into cpu-specific interrupt vector :
- init_cpu() :
- set_inkernel(0) :
- ker_start() :
(exit kernel via __ker_exit) :
:
cpu0 idle thread :
---------------- :
idle():
. if cpu0, memmgr.mcreate(procnto process) :
. cpu_start_ap(_smpstart) [start next cpu] :
- set SYSPAGE_ENTRY(smp)->start_addr ----> . atomically exchange start_addr with 0
. wait until all cpus have started . jump to start_addr
:
: _smpstart():
: . set stack pointer
: . jump to init_smp()
:
: init_smp():
: . set _cpupage_ptr to cpuN cpupage
: . if necessary, initialise cpuN VM data:
: - memmgr.init_mem(2) --> vmm_init_mem(2)
: . ker_start()
:
: (exit kernel via __ker_exit)
:
: cpuN idle thread
: ----------------
: idle():
: . cpu_start_ap(_smpstart) [if more cpus]
: . wait until all cpus have started
: OR
: <------------------------------------------- . cpu_started indicates all cpus have started
. SchedSet_r() to prio 0 . start system clock:
. Ring0(idle_release_stack, act) - clock_attach()
- ClockPeriod()
(entry via Ring0 kernel call) . ThreadCreate_r(..., start_kernel_threads, ...)
. SchedSet_t() to prio 0
idle_release_stack(): . Ring0(idle_release_stack, act)
. allocate new stack
. free original stack (entry via Ring0 kernel call)
. set KIP to loop()
(exit via __ker_exit) idle_release_stack():
. allocate new stack
. free original stack
. set KIP to loop()
(exit via __ker_exit)
At this point, the system contains the following threads:
The scheduler will run the kernel thread on one of the cpus; the other cpus will execute their idle thread. |